| Sl. | Risk Identification | Assessment of identified risk | Risk Severity | Risk Management |
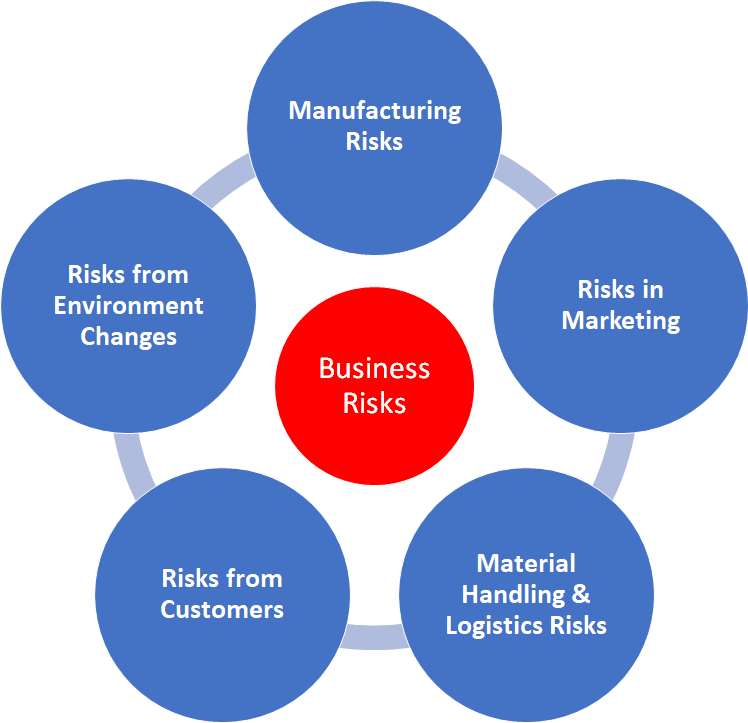
| 1 | Manufacturing Risks | | | |
| a | Non-availability of raw materials/ consumables | Company did not identify multiple sources for raw materials | High | Alternate vendors/ mines should be identified. |
| b | Breakdown in machinery | Equipments might face breakdown | High | Scheduled preventive maintenance should be done on time. Spare parts should be stocked. |
| c | Labour issues | Labour might go on a strike or might be unavailable for a few days due to a festival in the region or might get infected with a pandemic at the same time. | Low | Labour should be trained on multiple tasks to bring flexibility. Automation will also help in bringing down the dependence on manual labour. |
| d | Disruption in power, water supplies, gas, etc. | There might be disruption in public utilities. | Low | Back-up for a few days for power, water, gas, etc. should be ready with the factory. |
| e | Quality spills | The quality of the product might deteriorate. | Low | Staff should be encouraged to undertake quality improvement/ defect reduction projects. |
| 2 | Risks in Marketing | | | |
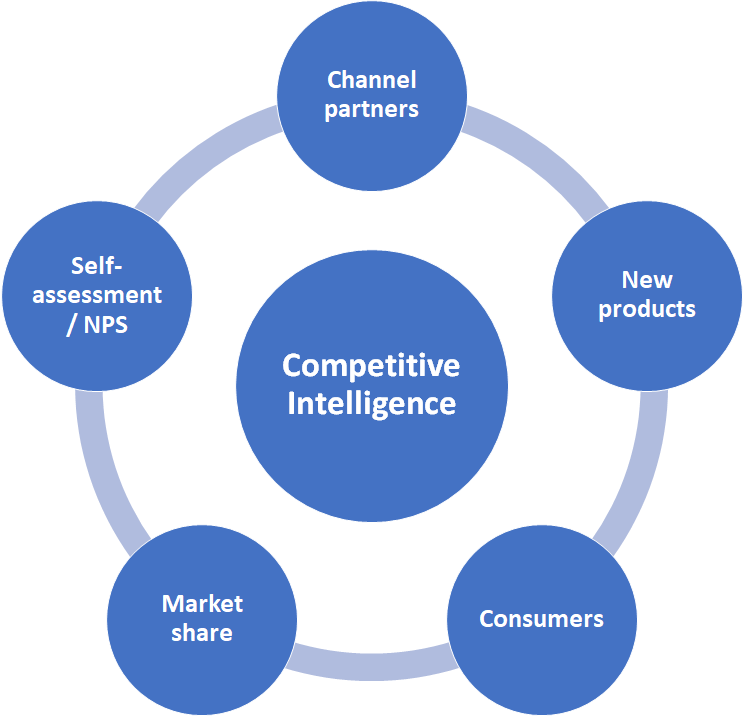
| a | Change in preference/ Technology disruption | Company did not foresee the changing preferences of consumers or a new player has entered which has changed the way customer was earlier doing transactions. | Medium | Company should routinely survey customer satisfaction with the company’s services/ products and track any changes in the market trends. |
| b | Inadequate promotion | Company might not be spending enough to build awareness for its products or to convert interest into sales. | Medium | Right mix of the various advertising media along with right timing needs to be strategized for maximum return. |
| c | Weak USP/ Incorrect marketing communication | Benefits highlighted for the product might not be resonating with the consumer or the message is not very clear. | Medium | Market survey should be done to understand stated as well as tacit needs of the customer/ influencer. |
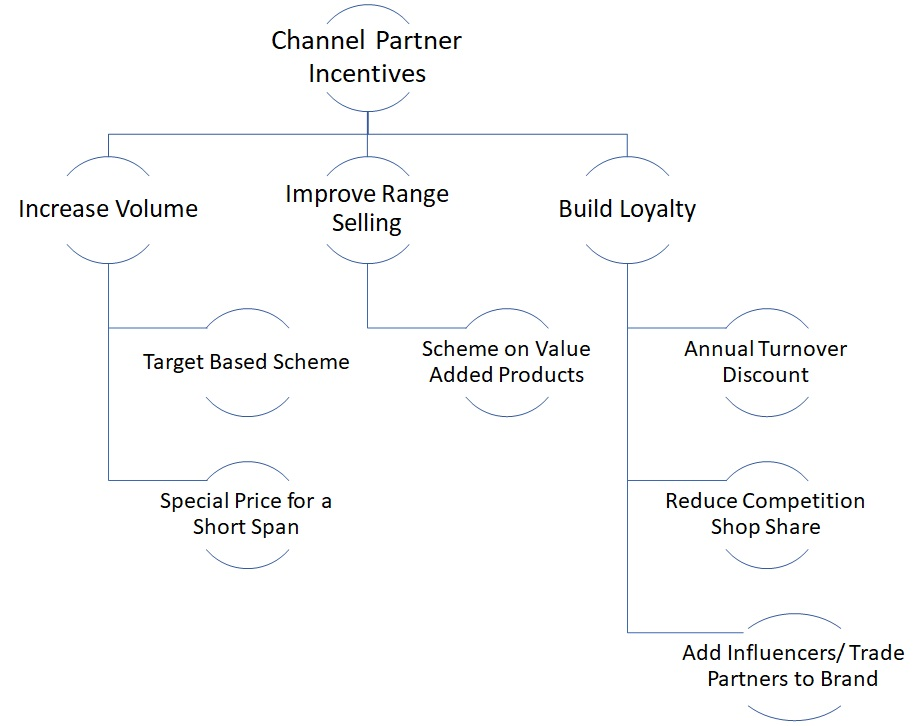
| d | Wrong choice of channel partners | Distributors and retailers selected might not be enterprising enough or have too little financial strength to promote the product | High | Financially stable, enthusiastic and preferably well-connected channel partners should be selected in a new market. |
| e | Misdirected advertisement | Marketing communications might not be reaching the correct target audience | High | Proper selection of advertising media should be done. |
| f | Wrong pricing strategy | Pricing might not have been set correctly for the customer to see correct value of the product | High | Pricing should be done keeping the value perception, competitor pricing and customer purchasing power. |
| g | Insufficient sampling | Company might not be distributing enough samples in the market or not | Medium | Provide enough samples and proof of concept in the market. |
| h | Poor after sales experience for the customer | Company might not have put in place a robust after sales customer support team or might not handhold the customer during installation | Medium | Dedicated after sales team should be built. This job should not be left to regular sales team. |
| 3 | Material Handling & Logistics Risks | | | |
| a | Carrying & Forwarding Agents (CFA) not executing orders not time. | CFAs might not be very efficient in servicing customers, leading to delays in customer service. | Medium | Payments done on monthly basis, so there is incentive for CFAs to perform well. |
| b | Inefficiency in clearing stock from rake point resulting in higher demurrage & wharfage charges | Difficult to monitor whether the CFA is working efficiently or not. | Medium | Logistics officers appointed in major markets to oversee such issues. |
| c | Claim of higher shortages & damages by CFAs | Difficult to inspect the entire incoming material, especially from rake. | Medium | Logistics officers appointed in major markets to oversee such issues. |
| d | Transport vehicle meeting with accidents on the way. | Possibility of trucks meeting accidents on the way due to negligence of drivers or other reasons. | Low | Drivers asked to stick to speed limits by the transporters. |
| e | Stealth of material by transporter | Trucks not tracked on the way to the destination. | Low | GPS tracking system installed on trucks. |
| f | Transport Unions strong in certain markets | Transport unions make secondary movement expensive or difficult in certain markets. | Medium | Complying with the local requirements |
| g | Natural calamity at godowns | Calamities like earthquake, floods, fire, etc. can strike the godowns and damage the material stored. | Low | Swift action taken by company to salvage the stuck material. |
| h | Illegal land/ restrictive areas | Depots can be located in areas where government might impose transport restrictions or land can be declared as illegal possession by landlord. | Medium | Marketing officers do due diligence while recommending godowns. All papers checked as per legal requirements. |
| i | Stealth of material from godowns | Difficult to monitor to godowns round the clock. | High | Material in depots audited periodically by marketing team, Cameras installed in godowns. |
| 4 | Risks from Customers | | | |
| a | Credit risk | Customers given much higher credit than the security deposits | Medium | Credit limits set and increased only after due diligence. |
| b | Outstanding | For some customers, outstanding is high and might be difficult to collect. | High | Constant follow-up done with customers for timely payment. Bank Guarantees available for major Non-Trade customers. |
| c | Material against concessional tax rates | Clients might not be able to give the required documentation in time. | Medium | Constant follow-up done with customers. |
| d | Supply issues | Supplies might not reach the customers as per promised schedule or not match their quality requirements. | Medium | Officer following up with the transporters and separate quality team functional. |
| e | Market price dilution by big wholesalers | Big wholesalers might try to average out their earnings. | Low | Discounts structured to not allow a big wholesaler influence market prices. |
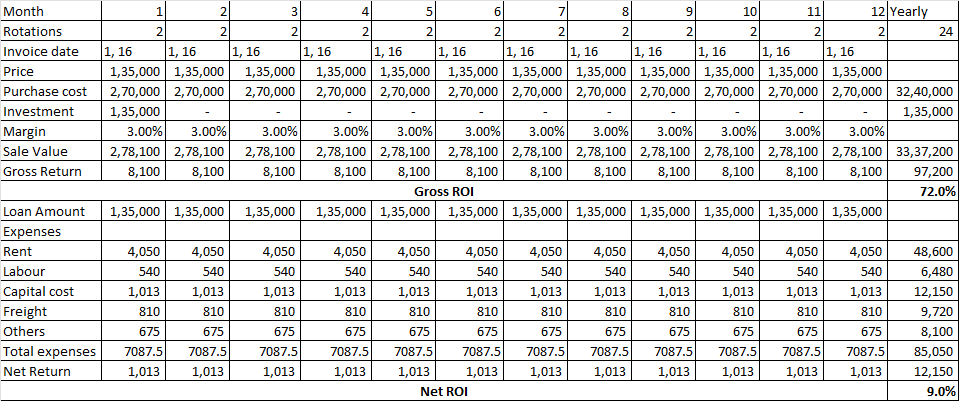
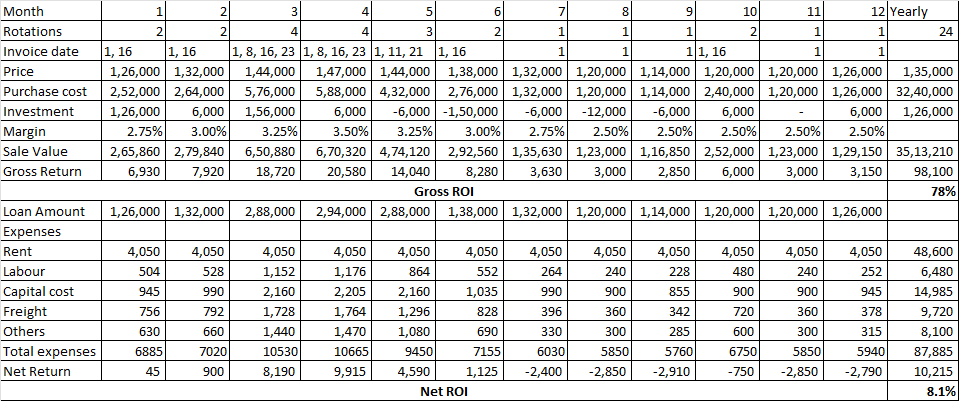
| f | Inadequate profit margin to channel partners | The competition might be offering better ROI for the channel partners. | Medium | Frequent checks by the company to assess the profitability of the channel partners need to be done. |
| 5 | Risks from Environment Changes | | | |
| a | New players entering the market | Can affect our market share and prices in the market | Low | Constant market feedback taken from regional offices. |
| b | Non-availability of other associated commodities like sand and gravel for cement, etc. | Can affect sales of commodity | Low | Constant market feedback taken from local marketing people. |
| c | Economic recession/ Natural calamity | Can affect spending power of consumers | Low | Company closely watching the economic scenario. |